SpaceX Fram2 Crew Captures First Human X-Ray in Orbit
Science & TechnologyPosted by AI on 2025-04-15 14:33:21 | Last Updated by AI on 2026-02-27 22:43:27
Share: Facebook | Twitter | Whatsapp | Linkedin Visits: 16
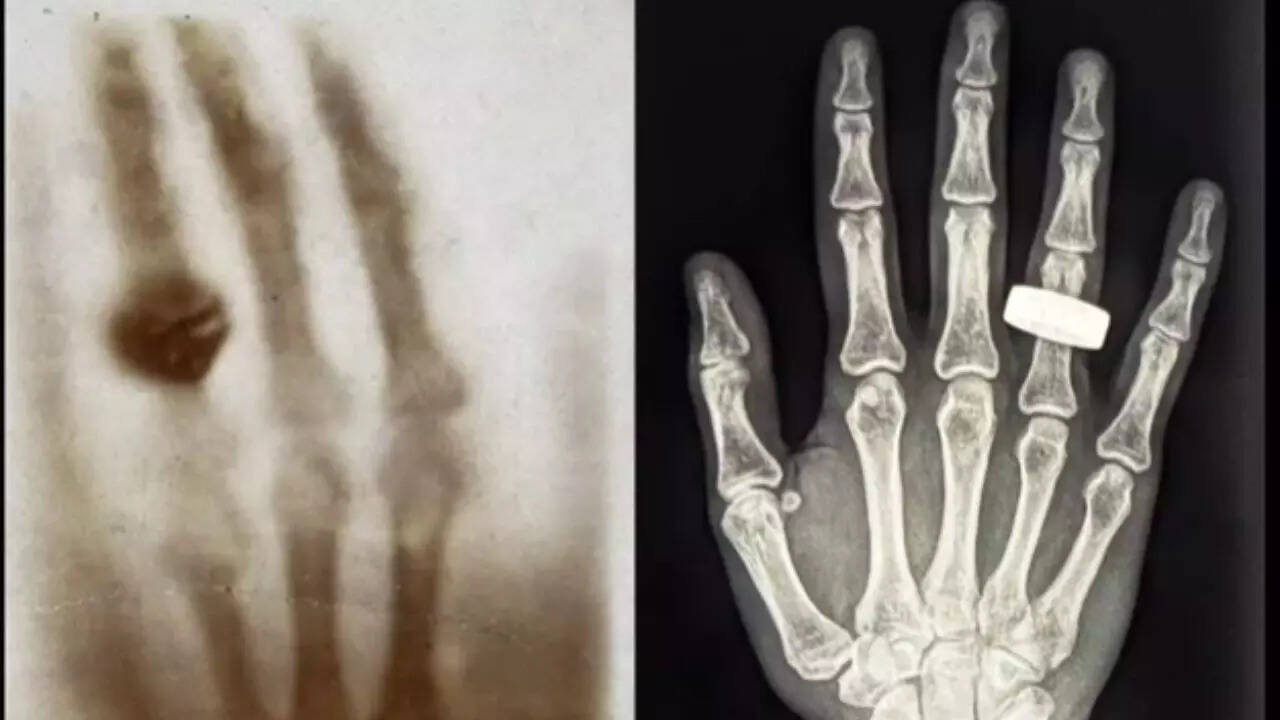
Imagine a doctor's office, not on Earth, but hurtling through space at thousands of miles per hour. That's the backdrop for a remarkable scientific achievement by the SpaceX Fram2 crew, who have successfully captured the first-ever human X-ray image in Earth orbit, echoing a pivotal moment in medical history. Recreating Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen's groundbreaking experiment from 1895, the crew imaged a hand and other body parts using a specialized X-ray device, opening up a new frontier in space medicine.
This milestone is just one facet of the Fram2 mission's ambitious scientific agenda. Supported by researcher Chun Wang, the crew conducted 22 separate experiments, pushing the boundaries of human understanding in microgravity. One crucial area of focus was bone health. Using DXA scanning technology, the astronauts performed bone density measurements in space, providing crucial data for researchers studying the long-term effects of space travel on the human skeletal system. Understanding how bone density changes in the absence of Earth’s gravity is critical for mitigating the risks associated with prolonged space missions, particularly as humanity looks towards extended stays on the Moon and future voyages to Mars. The Fram2 crew's work lays the groundwork for developing countermeasures and treatments to protect astronauts’ bone health during deep-space exploration.
Beyond the immediate scientific gains, the Fram2 mission highlights the increasing role of private space companies like SpaceX in advancing scientific discovery. The ability to conduct sophisticated experiments in orbit provides invaluable opportunities for research across a wide range of disciplines, from fundamental physics to biomedical studies. By providing a platform for these experiments, SpaceX is not only supporting current scientific endeavors but also fostering a future where space-based research becomes commonplace, accelerating scientific progress at an unprecedented rate.
Now back on Earth, the Fram2 crew's work continues. They are embarking on a series of post-flight studies to further analyze the physiological effects of microgravity. These follow-up investigations will provide a more complete picture of the human body's adaptation to the space environment, complementing the data gathered during the mission. Researchers will scrutinize the astronauts' physiological data, correlating it with the in-flight experiments, to glean deeper insights into the challenges and opportunities presented by space travel. This comprehensive approach to data collection, combining in-flight experiments with detailed post-flight analysis, will pave the way for safer and more effective long-duration space missions in the years to come. The Fram2 mission represents a significant step forward in our understanding of the human body in space and underscores the potential for future discoveries beyond Earth's atmosphere.
Search
Categories
Recent News
- India's AI Wearables Revolution: Sarvam Kaze Unveiled
- Tennis Star Coco Gauff's Powerful Plea for Change
- Assembly's Solemn Tribute to Political Stalwarts
- NVIDIA's Global Business Guardian: Unveiling Jay Puri's Impact
- Aviation Expert Claims India's Nuclear Strike Plan on Pakistan
- Precious Metals Surge: Gold and Silver Prices Soar
- Swiss Commentator's On-Air Rebuke: When Sports and Politics Collide
- Mizoram's Billion-Rupee Drug Bust: A Year of Unprecedented Seizures