Vera C. Rubin Observatory and Revolutionizing Astronomy in 2025
Science & Technology SciencePosted by NewAdmin on 2025-02-04 08:56:32 |
Share: Facebook | Twitter | Whatsapp | Linkedin Visits: 23
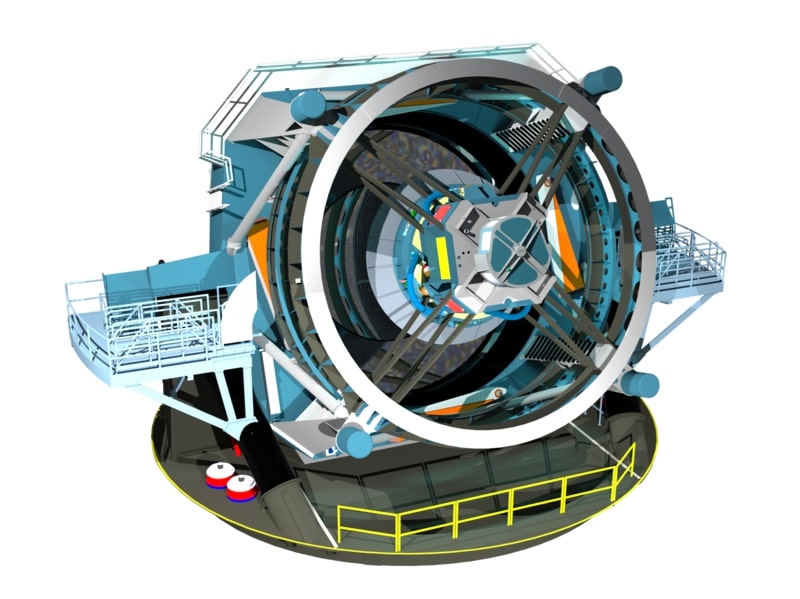
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, located in Chile, is set to revolutionize the field of astronomy starting in 2025 with its Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST), a project designed to capture an extensive dataset of the southern sky. The observatory features an advanced 8.4-meter telescope and an unprecedented 3.2-gigapixel camera, enabling it to take detailed images of the entire sky every few nights. Its primary scientific goals include studying dark matter and dark energy, tracking near-Earth objects (NEOs) for planetary defense, and observing phenomena such as supernovae, black holes, and transient events. One of the key features of the Rubin Observatory is the openness of its data; the LSST’s data will be publicly available, fostering collaboration between professional astronomers and global citizen scientists. Furthermore, the observatory’s vast datasets, which will amount to terabytes of information per night, will drive advancements in AI and machine learning, offering new tools to analyze astronomical data. The Rubin Observatory is expected to provide new insights into fundamental physics, the evolution of galaxies, and the nature of the universe itself, making it a cornerstone of modern astronomy.
The Rubin Observatory is expected to revolutionize our understanding of the cosmos. By mapping billions of stars and galaxies in unprecedented detail, it will provide insights into fundamental cosmic questions and inspire future generations of scientists. The data collected will not only deepen our knowledge of astrophysics but also benefit fields like artificial intelligence, as scientists develop new algorithms to analyze the vast amount of astronomical data.
As the observatory prepares for its first full operations in 2025, astronomers worldwide eagerly anticipate the groundbreaking discoveries it will enable.
Search
Categories
Recent News
- Messi's Return to Roots: Newell's Daring Vision for 2027
- Hyderabad's Crime Rate Drops, But Challenges Remain
- Ferry Service Expansion: A Boost for Tourism in Tamil Nadu
- 'Culture Clash' in Adelaide: Racial Tensions Rise Over Park Usage
- Peace Talks in Abu Dhabi: A Glimmer of Hope Amidst War's Shadow
- Global Risks 2026: Navigating a Decade of Uncertainty
- Chaos in Parliament: PM Modi's Address Postponed Amid Opposition Uproar
- Turkish Airlines Flight Makes Emergency Landing in Kolkata
Popular News
- Navigating IPO Market Dynamics Amid Volatility and Regulatory Changes
- Massive Worldwide Microsoft Outage Disrupts Multiple Sectors
- Panjapur Bus Stand to Reshape TNSTC Routes
- తెలుగుదేశం పార్టీ - పేదరికాన్ని నిర్మూలించడంలో వాగ్దానం
- Universities Embrace Remote Learning Technologies Amidst Ongoing Pandemic